Notepad is one of the simplest yet most versatile tools available in Windows. It’s a lightweight text editor that has been part of the Windows operating system for decades. Whether you’re a developer, a writer, or just someone jotting down quick notes, knowing how to get help with Notepad in Windows can enhance your productivity and streamline your tasks.
In this article, we’ll dive into how to use Notepad, troubleshoot common issues, and explore tips and tricks to make the most out of this handy tool. Let’s get started.
What Is Notepad in Windows?
Notepad is a basic text-editing program that comes pre-installed on every Windows system. It allows users to create and edit plain text files (files with the .txt extension). Despite its simplicity, Notepad can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Writing quick notes or lists.
- Editing configuration files for software and applications.
- Creating basic scripts or code in languages like HTML, CSS, or Python.
Whether you’re using Windows 10, 11, or an older version, Notepad remains a dependable tool.
Check Also: WordPad: Features, Uses, and How to Install in Windows 11
How to Open Notepad in Windows
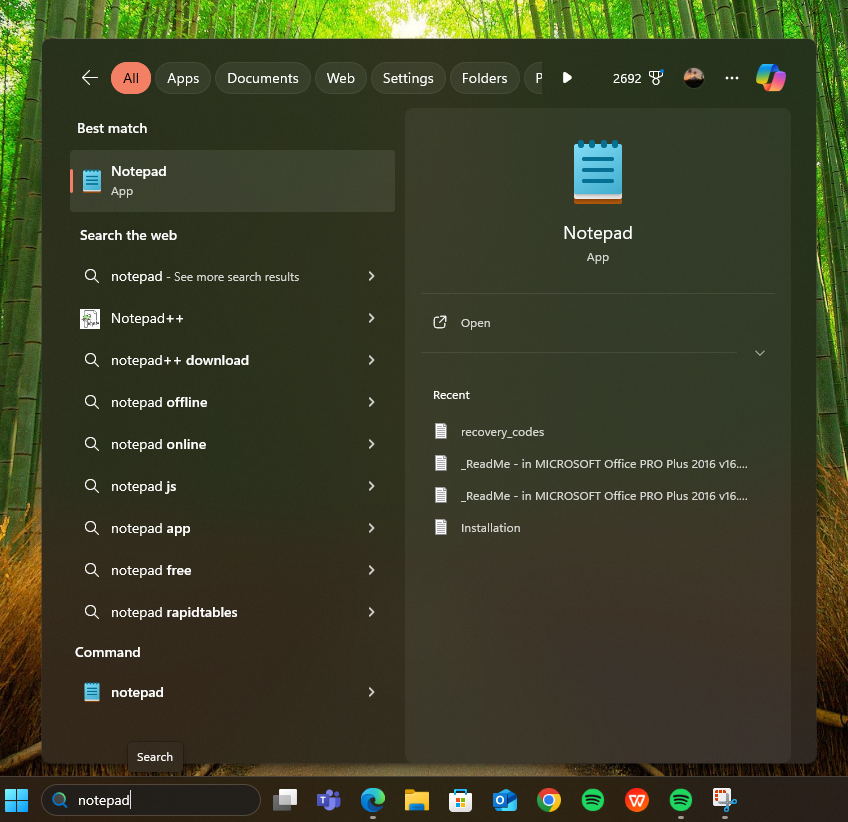
Method 1: Using the Search Bar
- Click the Start button or press the Windows key on your keyboard.
- Type “Notepad” in the search bar.
- Click on the Notepad app from the search results.
Method 2: Using the Run Dialog Box
- Press Windows + R on your keyboard to open the Run dialog box.
- Type
notepadand press Enter.
Method 3: From the Context Menu
- Right-click on your desktop or within a folder.
- Select New > Text Document to create a new file.
- Double-click the file to open it in Notepad.
Common Features of Notepad
Notepad may look simple, but it offers several features to make text editing easier:
- Word Wrap: Ensures text doesn’t run off the screen by wrapping it to the next line.
- Find and Replace: Quickly search for specific text or replace it with another string using Ctrl + F or Ctrl + H.
- Character Encoding: Save files in different formats, such as ANSI, UTF-8, or Unicode.
- Basic Formatting: Although Notepad doesn’t support rich text formatting, it’s perfect for plain text.
How to Get Help with Notepad in Windows
1. Notepad Won’t Open
If Notepad doesn’t open, try the following steps:
- Restart Your Computer: This simple step often resolves temporary glitches.
- Run as Administrator: Right-click on Notepad and select “Run as Administrator.”
- Reinstall Notepad:
- Open Settings > Apps > Optional Features.
- Search for Notepad, select it, and click “Uninstall.”
- Reinstall it from the same menu.
2. Unable to Save Files
If you’re unable to save a file, check:
- File Permissions: Ensure you have write permissions for the folder.
- File Name and Extension: Avoid using invalid characters or extensions.
- Storage Space: Verify that there’s enough disk space.
3. Missing Features
Notepad’s simplicity can sometimes be limiting. If you need advanced features, consider upgrading to Notepad++ or another text editor.
Tips and Tricks How to Get Help with Notepad in Windows
1. Use Keyboard Shortcuts
- Ctrl + N: Create a new document.
- Ctrl + S: Save the current document.
- Ctrl + P: Print the document.
- Ctrl + Z: Undo the last action.
2. Enable Dark Mode
In Windows 11, you can enable dark mode for Notepad:
- Open Settings > Personalization > Colors.
- Choose “Dark” as your default app mode.
3. Edit Large Files
Notepad is not ideal for very large files. If you’re dealing with large datasets or logs, switch to a more robust text editor like Notepad++.
4. Use It for Coding
Notepad is a great tool for quick coding. Save files with the appropriate extension (e.g., .html, .css, .py) and use them with other development tools.
Alternatives to Notepad
While Notepad is useful, you might need more advanced tools for specific tasks. Here are some popular alternatives:
- Notepad++: A feature-rich text and source code editor with syntax highlighting.
- Visual Studio Code: A powerful code editor for developers.
- Sublime Text: Known for its speed and customization options.
- Atom: A hackable text editor for developers.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I update Notepad in Windows?
Updates for Notepad are included in Windows updates. Make sure your operating system is up to date by checking Settings > Windows Update.
2. Can I recover unsaved Notepad files?
Notepad doesn’t have an autosave feature. However, you can:
- Check the temporary files folder.
- Use third-party recovery tools.
3. How do I change the default font in Notepad?
- Open Notepad.
- Click Format > Font.
- Choose your desired font, style, and size.
Conclusion
Getting help with Notepad in Windows is easier than ever. From understanding its basic functionality to troubleshooting common issues and exploring tips and tricks, you can make the most of this versatile tool. Whether you’re jotting down quick notes or editing code, Notepad remains a reliable companion for all your text-editing needs.
Read Also: